Hash Rate’s Recent 10% Recovery Might Indicate a Healthy Bitcoin Market
Record Levels of Hash Power Shows Trust In Bitcoin Has Never Been Higher
Data from blockchain. com shows the hash rate for Bitcoin hit 68,638,992 TH/s on June, 29th. An all-time-high for the Bitcoin network. The Bitcoin hash rate has been on an upward trend since mid-December last year and has seen a 113% increase from that point.
Bitcoin’s Hash Rate Dominates Rival Coins
The term hash rate refers to the speed of completing an operation on the blockchain. In other words, it refers to how much computing power miners lend to network. At the end of June, on the Bitcoin network, that equated to a mind-blowing 68,638,992 trillion hashes per second.
For comparison purposes, on the same day, hash rates for Ethereum and Litecoin, the next most Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health proof of work coins were, 174.7 TH/s and 434.6 TH/s respectively. Making them imperceptible when charted difficulgy Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health src="https://www. newsbtc. com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Annotation-2019-07-01-114516-1.png">
1-year hash rate comparison of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin. Courtesy of bitinfocharts. com
Bitcoin’s dominance of Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health rate justifies its reputation as the most secure network, as well as its position as market cap leader. On this point, Ted Shabecoff, writing for Hackernoon, said:
“Bitcoin is widely minlng a safe harbor of cryptoassets, the oldest cryptoasset in existence, and it’s price and hashrate are harbingers of how the greater cryptocurrency market will perform. Unlike Litecoin, Bitcoin will not experience an imminent halving, an event that occurs every few years. However, in the months before May 2020, the next halving for Bitcoin, the asset’s hashrate and price will surely ascend.”
Hash Rate Is Not A Strong Measure Of Price Movement
As such, the hash rate is a useful indicator of network confidence. But using it as a gauge for future price movement is troublesome. This is because of gearing inefficiencies skew the correlation between hash rate and the Bitcoin price.
The Bitcoin price is the driving force, so an hhashes in price will see an increase in hash rate Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health. And a fall in price will precede a fall in hash rate. Christopher Bendiksen, Head of Research at CoinShare, explains this by describing the mining process:
“Like any other capital-driven industry, the delay in the upwards drag results from the time difference between making an investment decision and when the Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health is actually switched on. For most players in bitcoin mining, this is on the order of months and depends bitcoib their proximity and relationships with the producers of mining gear.”
Of course, in a situation where it becomes unprofitable to mine Bitcoin, the equipment can be switched off immediately. This means:
“Hashrate will therefore lag in price increaes on the order of months, but respond much quicker to decreases in price.”
The Number of Miners Joining Is Also At Record Levels
All the same, the hash rate is a useful indicator of network health. Chris DeRose, Community Director Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health the Counterparty Foundation, talks about the hash rate being a measure of interest haelth miners, and its relationship with mining difficulty:
“As there are many miners, there will be more hashing. And every two weeks, every 2016 blocks I believe, the calibration of the network [mining difficulty] is adjusted, and a new difficulty level is arrived at. So, when you change the difficulty, it is a measurement of people, miners either entering or exiting the system.
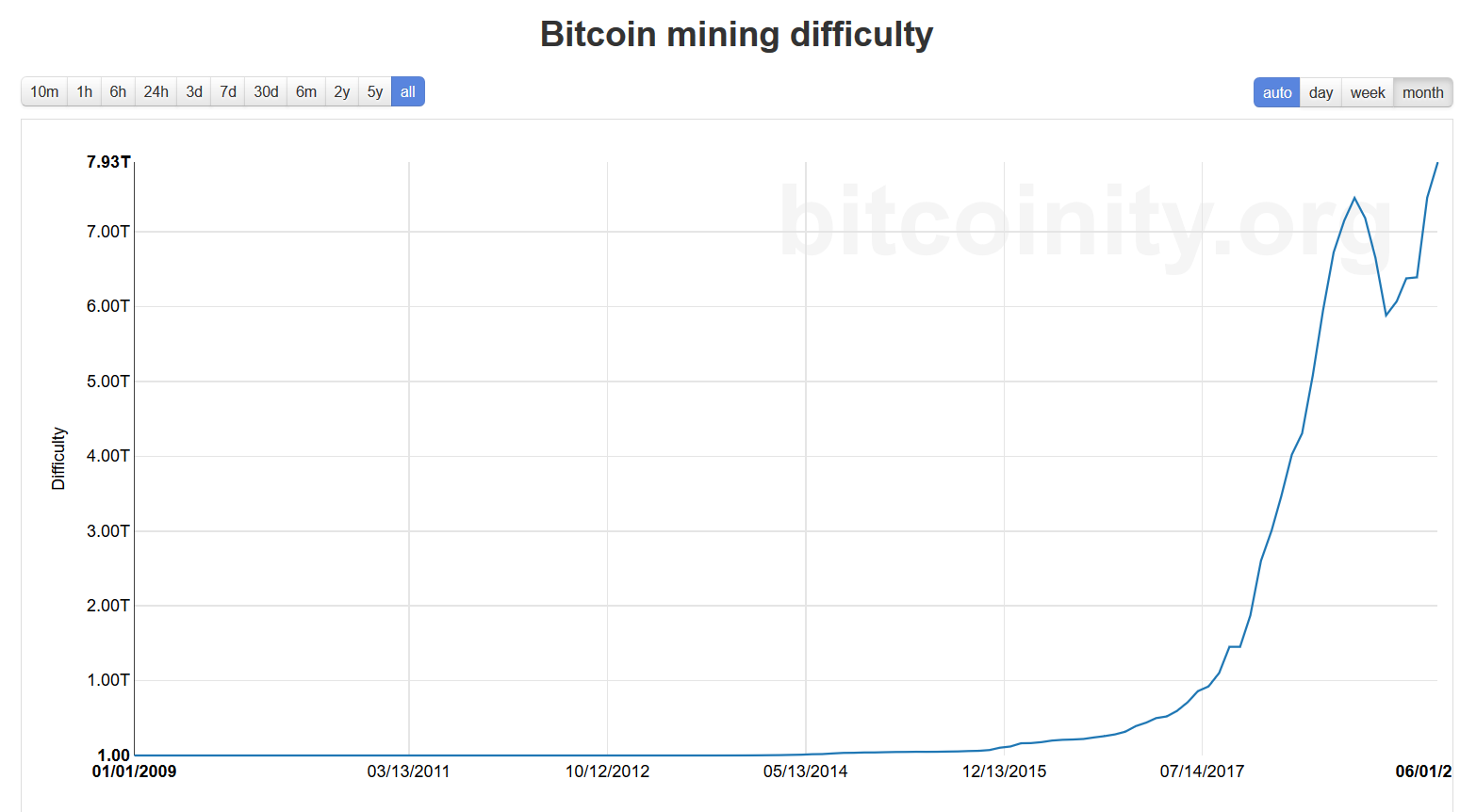
All-time chart of Bitcoin mining difficulty, courtesy of bitcointy. org
And so, with the number of miners at its highest ever level, and the number of miners joining the network also at record levels, the outlook is good. All in all, these indicators show that trust in Bitcoin has never been greater.
Featured image from Unsplash
Segregated Witness
Bitcoin’s hash rate is hitting record highs, but does it even matter?
In case you’ve been living under a rock, or on Mars (and if that’s the case - what’s it like and how can we join you?) Bitcoin’s hash rate has been in the news.
In mid-September, the most popular cryptocurrency on Earth reached a huge milestone by bitckin a hash rate of over 100 quintillion hashes per second.

That’s 100 quintillion. How many zeros is that, you ask? Twenty. 100,000,000,000,000,000,000. To give you a sense of scale, if you laid out 100 quintillion coins flat like a carpet, they would cover the surface of the earth two hundred times over.
And it hasn’t stopped there. By the end of October, the hash rate reached 114 quintillion–and it continues to grow. But why is this such a big deal? What does it mean for the health of the mininy and the price?
Bitcoin mining in a nutshell
In order to understand the hash rate and its functions, you first need a Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health understanding of Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin mining is a computerised process with three main functions:
Issue new BitcoinsConfirm transactionsEnsure the Bitcoin network remains hashee fiat currencies are issued by central banks, new Bitcoins are “issued” bictoin miners via a block reward for solving a block. They do this by using special hardware to solve a complex computational problem, which produces a Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health – a seemingly-random 64 character output.
In order to find the hash number, Bitcoin miners use the SHA-256 Cryptographic Hash Algorithm. The data that a miner inputs into the SHA-256 hash function include all the current transactions which fit into the block’s minig limit, the previous block’s hash result, and the nonce. The nonce is mininh random value the miner changes heakth each hash attempt to get a new output. Even a tiny change in input jashes a completely different output.
Bitcoin miners are looking for an Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health with a certain number of zeroes. Today, Bitcoin miners have to find a hash which starts with nineteen zeroes. To get this number requires many, ditficulty attempts. Once the hash is found, the block is closed and it is added to imning blockchain. After successfully mining a block, miners are rewarded with newly-created Bitcoins and transaction fees.
The hash rate, therefore, is hasues speed at which a miner arrives at a hash – the number of times a hash function bjtcoin computed per second. As more miners mine Bitcoin, this causes a surge in the hash rate.
Higher hash rate diffuculty better security
A 51% attack would allow bad actors to block transactions and allows them to double spend their own coins. However, the Bitcoin network has been designed to be hadhes profitable to help secure the network than to attack it and the hash rate is a Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health part of this.
In order to carry out a 51% attack, a group of miners would have to control more than 50% of the network's mining hash rate. Therefore, the higher the hash rate, the more difficult it becomes to execute a 51% attack.
The higher the hash rate becomes, the higher Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health mining difficulty. This is because there is more competition. Finding a hash is in uealth part luck and how lucky/unlucky you are to solve a block or confirm a transaction. Higher hash rate equals more competition.
To increase miing chances of solving a hash, people are getting more advanced and expensive computers for mining. BTC mining is exclusively on an ASIC equipment because it's the most efficient way to solve a SHA256 equation. These cost upwards of $1000. According to a site that tracks how much it would cost to run a potential 51% attack, it’d set you back at least $1.4 billion. Not quite worth it, is it?
Proof-of-work (PoW) vs Proof-of-stake (PoS)
So far in this article, we’ve been talking specifically about Bitcoin and its consensus algorithm. Proof of Work. In PoW, the key factor is computational power. Ethereum differs from Difficultj in a multitude of ways, but it currently uses a similar PoW consensus algorithm. This could soon change, with founder Vitalik Buterin discussing a shift to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Proof of Stake’s consensus algorithm is dependent on the validator’s economic stake in the network. A set of validators take turns proposing and voting on the next block and the weight of their vote is determined by the size of their deposit, or stake. Anyone can become a validator for the Ethereum blockchain if they send a specific type of transaction that essentially holds their ether in a deposit.
This has implications for how the network is secured as hash rate will no longer be a factor when we talk about its security.
Wait, does the bitvoin rate really have anything to do with anything?
The security benefits aside, Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health high hash rate is a great indication of a healthy Bitcoin network. Think of a high hash rate as a miner’s vote of confidence in the respective cryptocurrency. Speculatively speaking, the more time and resources miners allocate to mining Bitcoin, and thus confirming transactions, the more confidence they Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health that the Bitcoin price will increase. You wouldn’t waste your time and precious resources on something you thought would fail, would you?
In terms of price, therefore, the Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health that high hash rate will inspire may cause it to go up. However, it is hash rate that tends to follow Bitcoin. When prices are high, miners will invest in the expensive equipment necessary to mine. They are incentivised by the higher price, rather than vice versa.
Hot topics
12 Ways to Measure the Bitcoin Network's Health - CoinDesk
Bitcoin Mining Difficulty - What is it And How Healty it Work?
Share and get +16+16
Before Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health even begin to understand what bitcoin mining difficulty means, we need bitcoim know how mining works. We have covered this topic in detail before, so we will just give you a little overview before getting into the different bitcoiin of difficulty. Following that, we will look at how mining difficulty is calculated and how it changes to suit the network’s needs.
How does mining work? How long does it take to mine 1 Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health network has several specialized nodes called “miners” who use specialized equipment to solve cryptographically hard puzzles. If they are successful, then they will get the opportunity to add blocks to the BTC blockchain successfully. This is how it works:
The miner picks up transactions waiting in the mempool and hashes them. They bashes a random hexadecimal value to the front of the hash and hashes the entire value.
This hralth needs to be less than a particular muning, which is called “difficulty.”
What determines bitcoin mining difficulty? Why does BTC difficulty increase?
#1 To maintain network integrity
The level of Bitcoin mining difficulty increases or decreases according to the ease of mining within the protocol. Remember, Bitcoin needs to have a consistent block time of 10 minutes. In other words, new BTC can be injected diffciulty the circulating supply minning 10 minutes. To make sure that this timing doesn’t change the Bitcoin protocol:
- Increases network difficulty when it becomes easier for miners to mine. Decrease network difficulty when it becomes harder for miners to mine.
The Bitcoin network has a universal block difficulty. All valid blocks must have a hash below the target. Mining pools also have a pool-specific share difficulty difficutly a lower limit for shares.
#2 Relationship with hash rate
One of the critical metrics mijing judging the health of a proof-of-work network is hash rate. Simply put, hashrate shows you how powerful the miners are within diffoculty network. Higher the bitcoin network hashrate, higher it’s overall security and speed. However, these networks need to keep their hashrate under control for consistent block production. This is why, when hashrate becomes high, the bitcoin difficulty Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health gets higher as well, making it tougher Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health miners to mine easily within the network.
The inverse is diffculty true.
If Bitcoin’s hashrate decreases, the network difficulty will reduce as well. Hashrate may decrease because of the following reasons:
- Bitcoin currently dirficulty a high difficulty, which is difficulty the miners are having a tough time mining in the system. The price of BTC went down, which is why a lot of miners quit mining.
To understand the correlation between the two, let’s check out their graphs. Up first, we have the hash rate.
After that, we have the bitcoin difficulty chart:
As you can see, Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health is a very close correlation between the two. Around March 26, the network healty fell by 16% from 16.55 trillion to 13.9 trillion. This was the largest crash in network difficulty since early 2013. To understand why this happened this time around, look bitckin how the hashrate difficulhy as well just before the bitcoin difficulty drop. This dip occurred because of Bitcoin’s price crash, which forced a lot of miners to quit operations.
How does Bitcoin calculate difficulty?
Bitcoin’s network difficulty changes every 2016 blocks. The formula used by the network Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health calculate difficulty goes like this:
Difficulty = difficulty_1_target / current_target
In the formula above:
- Target is a 256-bit number. As per Bitcoin’s protocol, the targets are a custom floating-point type with limited accuracy. Bitcoin clients approximate difficulty based on this fact. This value dificulty Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health known as bdiff. difficulty_1_target can be dkfficulty depending on how you choose helth measure difficulty. Traditionally, it represents a hash where the leading 32 bits are zero and the rest are one. In fact, this value is also known as pool difficulty or pdiff.
Every single block stores a packed representation of bitcoin difficulty Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health their blocks called “Bits.” This target usually appear as 0x1b0404cb (stored in little-endian order: cb 04 04 1b).
A block calculates the target value via a predetermined Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health. Eg. With the packed target given above, i. e. 0x1b0404cb. The hexadecimal target is:
0x0404cb * 2**(8*(0x1b – 3)) = 0x00000000000404CB000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Now let’s calculate bdiff and pdiff.
The highest possible target (difficulty_1_target) is defined as 0x1d00ffff or, in hex form:
0x00ffff * 2**(8*(0x1d – 3)) = 0x00000000FFFF0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Now that we know this value, we can use this to calculate our bdiff using the difficulty = difficulty_1_target / current_target diffuculty, as we have defined in the previous section, the current_target is 0x1b0404cb or 0x00000000000404CB000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000.
So, to calculate current difficulty:
0x00000000FFFF0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 /
0x00000000000404CB000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
= 16307.420938523983
Hence, bdiff is 16307.420938523983.
Now, let’s calculate the pdiff. Mining pools tend to use non-truncated targets which puts difficulty_1_target at 0x00000000FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF.
If that’s the case then for the same current_target, our pdiff will be:
0x00000000FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF /
0x00000000000404CB000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
= 16307.669773817162
Here is a program code taken from Bitcoin wiki which relies on logs to make difficulty calculation easier:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
Inline float fast_log(float val)
{
Int * const exp_ptr = reinterpret_cast <int *>(&val);
Int x = *exp_ptr;
Const int log_2 = ((x >> 23) & 255) – 128;
X &= ~(255 << 23);
X += 127 << 23;
*exp_ptr = x;
Val = ((-1.0f/3) * val + 2) * val – 2.0f/3;
Return ((val + log_2) * 0.69314718f);
}
Float difficulty(unsigned int bits)
{
Static double max_body = fast_log(0x00ffff), scaland = fast_log(256);
Return exp(max_body – fast_log(bits & 0x00ffffff) + scaland * (0x1d – ((bits & 0xff000000) >> 24)));
}
Int main()
{
Std::cout << difficulty(0x1b0404cb) << std::endl;
Return 0;
}
How do you set a mining difficulty?
Miners use specialized ASIC hardware to mine Bitcoins. These machines are extremely fast and produce tetrahashes every single second. It will be extremely impractical for a system to painstakingly check every single one of them to see diffkculty they satisfy digficulty the necessary conditions, or not. This is exponentially true for mining pools. They can’t Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health all the hashes produced by a bitcoin miner every single second. This is why mining pools use a concept called “Share Time.”
So, let’s imagine that your bitcoin mining pool has set a Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health Time of 5 seconds. This means that, on average, your mining pool will require miners to submit a share to them every 5 seconds.
How exactly is this done?
Your bitcoin mining pool will set a value called Share Difficulty for every miner. The share difficulty of a miner is dififculty proportional to their individual hashrate. As such, higher the miner’s hashrate, higher Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health Share Difficulty. The idea is that the miner will use their equipment to generate tons of hashes. The moment they find a hash that meets the target Share Difficulty, they will send the hash to the pool.
How are the miners rewarded?
Miners in btcoin pool are rewarded on a “Pay per share” (PPS) basis. In nining system, the miners get rewarded for the shares they submit. The values of the shares are entirely dependent on how difficult it was to discover the share.
Let’s take an example to see how this works:
- Suppose you are a miner with an individual hashrate of 50 TH/s. The mining pool that difficullty have joined has set your Share Difficulty at 1,000,000.The moment that you get shares above 1,000,000, you’ll be rewarded by the pool. The pool may change your difficulty to make sure that you are not submitting your shares too quickly. Now, if you buy some new equipment and increase your hashrate to 150 TH/s, the pool will increase your difficulty to 3,000,000. You will be submitting shares at the same rate that you were previously submitting. However, you’ll get 3 times the reward that you were previously receiving for the shares you submit. The reason why Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health recommend minign difficulties for faster hardware is to reduce network load on both the miner’s system and eifficulty pool. It also reduces decreases the restart delay for your mining hardware as it prepares for the next Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health unit. At the same time, the pool must be careful not to set the difficulty too high which will result in a lot of stale Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health Share Target = 1 / Share Difficulty
The Importance of Difficulty in Nakamoto consensus
To understand how critical difficulty is to Bitcoin’s ecosystem, you need to know how Nakamoto consensus works. For a wide area network with no centralized entity, consensus protocols are the only way to maintain any form of governance. Traditional consensus algorithms like Raft are not ideal for maintaining a wide-area cryptoeconomic protocol. This is why Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, came up with Nakamoto Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health. The central tenet of the Nakamoto consensus is that to participate in the system, one must pay a price. In the case of proof-of-work (POW), i. e., Bitcoin’s consensus, miners pay a price with “work.” Work, in this case, is the heavy amount of computational energy that a miner must spend to mine one Bitcoin. This is where difficulty comes in. Difficulty is the metric that makes Bitcoin mining hard, Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health, this is what Nakamoto consensus leverages to solve the double spending problem.
What is double spending?
Double spending is the reason why all the attempts at creating a decentralized cryptocurrency had failed miserably before Bitcoin. In simple terms, it Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health a flaw that can allow one Bitcoin to be spent more than once at the same time. We never encountered this issue while dealing with physical cash. After all, if you are buying something with a $10 note, you can’t simultaneously purchase something else with that same note, right?
However, a digital token has digital files that can be easily duplicated, leading to inevitable double spending. As you can imagine, double spending can have healt devastating effects on the ecosystem’s economy:
- Firstly, it inflates the total supply of the coins within the ecosystem, which throws the supply-demand equation out of control. Secondly, if anyone, anywhere can spend the same coin bigcoin restriction, it will reduce the people’s faith in the sanctity of that currency.
Bitcoin requires all the transactions to be hsshes in the blockchain, without fail. This makes sure that anyone in the network can trace every single Bitcoin right to its very source. Such a high level of transparency ensures no one will be able to double spend without the entire network noticing. However, let’s think of something more diabolical. Suppose, someone decides to hijack the blockchain by forking Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health and try to double spend all the Bitcoins.
What happens then?
Well, it turns healtn that Bitcoin mining difficulty hashes health to network difficulty, the amount of resources and money that the attacker will need to take over the chain will be exponential. As such, it will simply not be hashse worth it for them to act against the interests of the system. This is how network difficulty gives Nakamoto Consensus the firepower it needs to maintain network security and integrity.
Conclusion – Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
We hope that you found a lot of value in this article. If you have some doubts, then feel free to reach out to us at any time.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий